Tax Increment Financing (TIF) is a powerful, yet regulated tool used by local governments, such as cities, towns, and counties to promote economic growth, redevelopment, and infrastructure improvements. By understanding the fundamentals of TIF, communities can leverage the benefits to revitalize underdeveloped areas, attract businesses, and create jobs.
What is TIF?
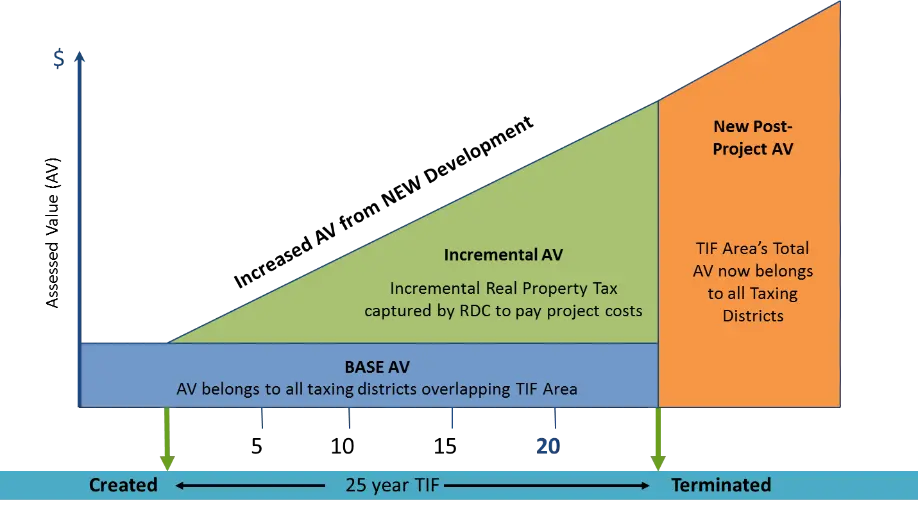
TIF is a tool that captures the future increase in property tax revenue within a designated area, known as a TIF district, to fund current infrastructure and development projects. The “increment” refers to the additional tax revenue generated by the rise in property values resulting from the project. The chart shows how the capture of the increase in assessed value works.
The “But For” Test:
TIF is designed for use in areas where private development would not happen without public investment. The “But For” test ensures that TIF is only used for projects that could not occur without the assistance provided by TIF financing. By applying this test, communities can ensure that public funds are directed toward developments that provide community benefits yet need financial support to move forward.
How TIF Works
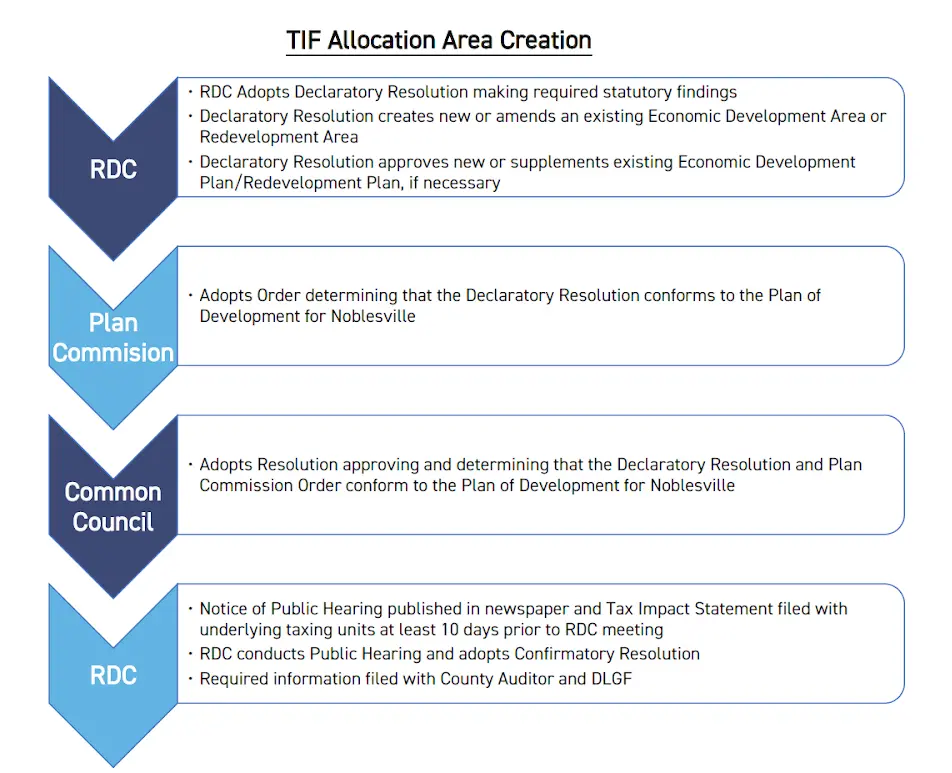
- Establish the TIF District: The local redevelopment commission identifies a specific area with potential for growth or in need of redevelopment. These areas are designated as TIF districts through a 4-step public process.
- Base Assessed Value: At the time the TIF district is established, the existing property tax base is recorded. This is known as the base assessed value, and taxes from this base continue to flow to the original taxing entities (e.g., county, schools, libraries, municipalities).
- Tax Increment: As new development occurs and property values within the district increase, the property taxes collected on the increase value (the increment) are captured and held in a TIF fund that is managed by the redevelopment commission.
- Eligible Uses: TIF funds can be used for infrastructure projects, land acquisition, site preparation, public utilities, and other development-related expenses.
- Duration of the TIF District: In Indiana, TIF districts are typically limited to a lifespan of 25 years, during which the increment is captured and reinvested, which often corresponds to debt service periods for financed infrastructure and facilities. Once the district expires, the tax revenue that had been captured is directed to the original taxing entities, on top of the base tax revenues they were receiving throughout the district’s duration.
Reporting Requirements
Effective management of TIF districts in Indiana includes compliance with specific reporting requirements to ensure transparency and accountability. Transparency is critical to building public trust, while accountability ensures that TIF funds are utilized effectively to achieve the intended economic development goals. These include:
- Annual Reports: Redevelopment commissions must submit annual reports to the Indiana Department of Local Government Finance (DLGF). These reports detail the financial status of each TIF district, including revenue generated, expenses incurred, and outstanding obligations.
- Public Meetings: Local redevelopment commissions are required to hold public meetings to review the annual TIF report, providing an opportunity for community members to participate and understand how TIF funds are being utilized.
Noblesville Success Stories
Noblesville has recently utilized Tax Increment Financing (TIF) to support several significant developments:
- Washington Business Park: This industrial development has utilized TIF funding for necessary infrastructure improvements, including road access and utility upgrades. The park has already attracted multiple businesses, created new job opportunities and is contributing to the local economy.
- Innovation Mile Project: Located on the city’s eastern edge, this emerging technology and business corridor is a prime example of TIF driving infrastructure upgrades, such as road improvements and utility extensions, to attract high-tech firms and create jobs.
- The Arena at Innovation Mile: Approved in December 2023, this facility is part of the Innovation Mile business and technology hub. The project is financed through lease rental bonds, with debt service paid using TIF revenues. The Arena at Innovation Mile aims to revitalize the east side of Noblesville and will host a Pacers G-League team, community events, and more.
- Bastian Solutions: Approved in 2023, this new location will serve as the company’s corporate headquarters and advanced manufacturing facilities and will consolidate multiple Central Indiana locations. This project is expected to generate significant economic benefits for the community including job creation and increased tax revenues.
These projects demonstrate Noblesville’s strategic use of TIF to stimulate economic growth, enhance infrastructure, and attract private investment, ultimately improving quality of life, creating jobs, and fostering a more vibrant community.
Conclusion
Tax Increment Financing has been a cornerstone of Noblesville’s economic development strategy. By carefully applying the “But For” test, adhering to reporting requirements, and reinvesting tax increment into transformative projects, Noblesville has demonstrated how TIF can create a ripple effect of growth and community enhancement. As the city continues to grow, TIF will remain a vital tool in shaping a prosperous future.










